1980s Vintage Computers
|
Connectors and leads |
Connectors and leads
Several vintage computers have custom connectors for
video and cassette recorders and so selecting the right
lead can be tricky. This guide covers some of the
computers and devices I have used.
Cassette connector
Most computers supported ordinary mono cassette recorders. This section does not cover computers that used special cassette decks such as the Commodore PET or the Atari 600XL.
All connectors shown are sockets viewed from outside the
device.
Tandy TRS-80 Model 1
Tandy TRS-80 Color Computer 2
Dragon 32
The Tandy TRS-80 model 1 was one of the earliest home
computers with a cassette connector, and so the pin-out
was copied by many others.
5-pin DIN socket:
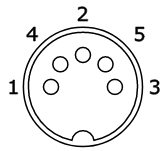
1 & 3 - remote
2 - ground
4 - phones (input to computer)
5 - mic (output from computer)
NEC PC-8001
7-pin DIN socket:
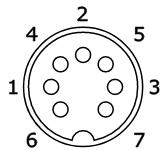
2 - ground
4 - mic (output from computer)
5 - phones (input to computer)
6 & 7 - remote
Acorn BBC micro and Master
7-pin DIN socket:

1 - mic (output from computer)
2 - ground
3 - phones (input to computer)
6 & 7 - remote
Research Machines Link 480Z
7-pin DIN socket:

1 - mic (output from computer)
4 - ground
6 - phones (input to computer)
3 - +5V (for relay driver)
2 - recorder 1 control (TTL output)
7 - recorder 2 control
The 480Z can switch betwen two cassette players under software control.
Cassette leads
Home cassette recorders have a 3.5mm socket for output to headphones or earpiece, and a 3.5mm socket for a microphone. Several also had a 2.5mm socket for remote control (ie only play when a short circuit is made).
If using a stereo cassette player (or a modern computer with a headphone socket) then use suitable adapters to use only one channel from the headphone output, and if possible both channels in parallel for the microphone inputs.Leads are easily purchased for the Dragon 32 and BBC micro. The NEC PC-8001 pin-out was copied for the MSX standard so is also easy to find, or if remote is not needed a Dragon 32 lead can be used with the mic and phones plugs the other way round.
Video Connector
There are two main types of video connectors, those provide a composite video output (where the video signal is mixed with sync signals) and those that provide separate video and sync outputs. Monochrome video always uses a composite output connector, whilst colour can use either.
Video output signals from a computer have to be at the
right voltage and frequency for a particular monitor
input, or in some cases a computer with a higher voltage
output the signal can be attentuated with resistors. Video
convertors or adapters are also available (eg RGB to HDMI)
but these are beyond the scope of this page, I will only
describe passive leads that work with monitors I have
access to,
Tandy TRS-80 Model 1
This provides monochrome video only.
5-pin DIN socket:

4 - composite video
5 - ground
1 - +5V (provided for optional UHF modulator)
Dragon 32
This provides compoisite video (PAL colour) and sound output on the same 5-pin DIN socket:

2 - ground
3 - composite video
1 - sound out
NEC PC-8001
This has two video outputs for monochrome or colour.
Monochrome - 5-pin DIN socket:

3 - composite video
2 - ground
1 - +12V
5 - lightpen input
Colour - 8-pin DIN socket (270°):
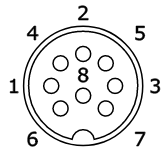
2 - ground
4 - HSYNC (inverted)
5 - VSYNC (inverted)
6 - red
7 - green
8 - blue
1 - +12V
3 - colour clock
Acorn BBC micro and Master
6-pin DIN socket:
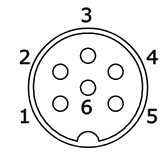
1 - red
2 - green
3 - blue
4 - sync (composite H+V)
5 - ground
6 - +5V
Signal levels are TTL with positive sync by default (negative sync can be
set with link S31). Frequencies are 50Hz vertical
(frame) and 15.625kHz horizontal (line).
Tatung Einstein TC-01
This computer has internal jumpers to configure the video output to either RGB or YUV colour mode. The YUV setting can also be used for a monochrome output.
6-pin DIN socket:

RGB mode (nb same as Acorn computers above):
1 - red
2 - green
3 - blue
4 - sync (composite H+V)
5 - ground
Signal levels are 1V peak-to-peak, so the output is lower than from a BBC micro. Frequencies are 50Hz vertical and 15.625kHz horizontal.
YUV mode:
1 - V
2 - Y + sync
3 - U
5 - ground
Signal levels are 0.6V (Y and U) or 1V (Y + sync) peak-to-peak.
For a monochrome monitor use pins 2 (composite video) and 5 only.
Atari 800XL
Following is for the UK PAL model. Provides either
composite colour video, or Y+C video (combined on S-video
input on a monitor or TV). Socket also provides a sound
output.
5-pin DIN socket:

2 - ground
4 - composite video
3 - sound out
1 - Y + sync video
5 - C video
Commodore C64 and C128
Provides either composite video or Y+C video out, and sound in and out connectors.8-pin DIN socket (262°):
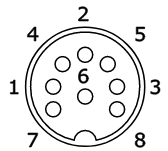
1 - Y + sync video
2 - ground
3 - sound out
4 - composite PAL video
5 - sound in
6 - C video
8 - +5V
For a monochrome monitor use pins 1 (composite video) and 2 only.
Research Machines Link 480Z
This has two video outputs for monochrome or colour.
Monochrome - 6-pin DIN socket:

1 - composite video
2 - ground
5 - sound out
3 -
VSYNC (Frame)
4 - HSYNC (Line)
6 - video (when using VSYNC and HSYNC)
The manual refers to pin 6 as 'wireframe video', exact signal levels to be confirmed.
Colour - 8-pin DIN socket (270°):

1 - sound out
2 - composite sync (inverted)
3 - red
4 - ground
5 - blue
6 - green
7 - HSYNC, Line (inverted)
8 - VSYNC, Frame (inverted)
Levels are TTL. Exact format to be confirmed.
This page was last revised on:03/05/23